HVDC Circuit Breakers
Home | About | Technologies | Report Download | Contact Us
Technologies > Breakers Within HVDC Grids
We previously compared two technologies, CSC and VSC and saw that
VSC is the ideal technology for multi-terminal networks.
In CSC technology (point to point transmission) once a fault occurs the whole
station is shut down. That cannot happen in a DC grid and that is why DC breakers
that can interrupt one part of the network are required.
We will examine the interruption process in three different DC grid
topologies. Large offshore wind farm grids will be used as an example.
1. Point to Point Topology
In a grid with multiple point to point connections, once a fault
occurs a single line can be disconnected by simply using the AC circuit breakers
on the converter side for each station.
2. Ring Topology (fig.10)
The stations are connected in a ring. Once a fault occurs the two
HVDC circuit breakers that are connected to the fault are opened. When the fault
current is interrupted and reaches zero the isolators can isolate the faulted station
and then the circuit breakers can close again. The advantage is that if AC breakers
were used all the stations will have to turn off.
3. Star Topology (fig. 11)
The stations are all connected to a central node. Once a
fault occurs the line with the fault can be disconnected using the HVDC circuit
breakers, compared to CSC where both the faulty station and the central node would
have to disconnect.
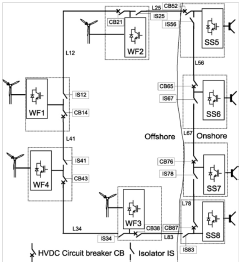
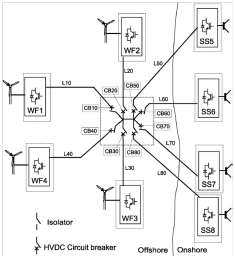
Figure 10: Ring topology
Figure 11: Star topology [2]
Multi-terminal HVDC networks can offer some clear advantages. With the use of a DC grid, the number of converters required is less than that of multiple point to point HVDC links and that decreases investment costs and AC to DC conversion losses. Furthermore, energy trade is made much easier with the use of a grid and power imbalances can be handled more efficiently. On the other hand, compared to an AC grid, DC grids are much more efficient, less costly, stations are much smaller than the respective AC ones and even though installation costs are high, these costs will balance out with time.